Introduction to Webb - A cross-chain zero-knowledge messaging protocol
A cross-chain zero-knowledge messaging protocol

Overview

Zero knowledge proofs are one of the most powerful technological primitives of this decade. They allow us to scale blockchains and build privacy-preserving technology for financial, identity, and social applications. Undeniably, this technology will usher in a new frontier of the internet in this decade.
At Webb, we’ve been researching and developing cross-chain technology that leverages zero-knowledge proofs and are excited to announce what we’ve designed.
We are building the cross-chain zero-knowledge messaging layer for blockchains.
The Tangle Network

A core infrastructural component of Webb’s zero-knowledge messaging layer and a core piece in the development of any future zero-knowledge cross-chain application using Webb’s tools is the Tangle Network. The Tangle Network is a threshold-signature based blockchain that offers secure bridging and message passing capabilities. It’s validators participate in a recurring multi-party computation to refresh and grow the security of any connected application leveraging its threshold-signatures.
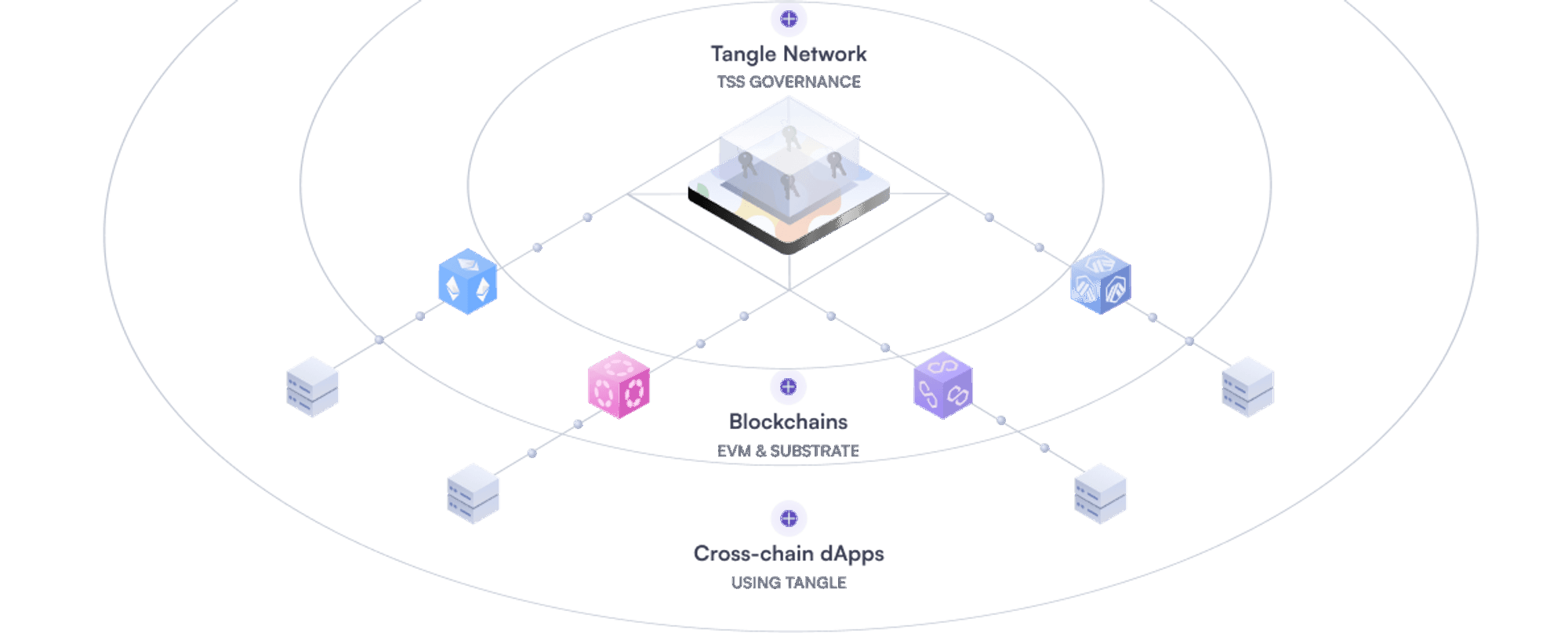
The Tangle Network is built as a Substrate standalone chain and is geared to serve users and operate bridges between any EVM, Substrate, and Cosmos based blockchain, with plans to expand in the future to any other compatible blockchain ecosystem with a strong privacy need.
There are a variety of ways to get involved as a node operator or relayer operator if you’re interested in contributing to the cutting edge of MPC and blockchain technology.
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/tangle-network/overview/
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/tangle-network/node-operators/quickstart/
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/relayer/overview/
The Hubble Bridge Protocol
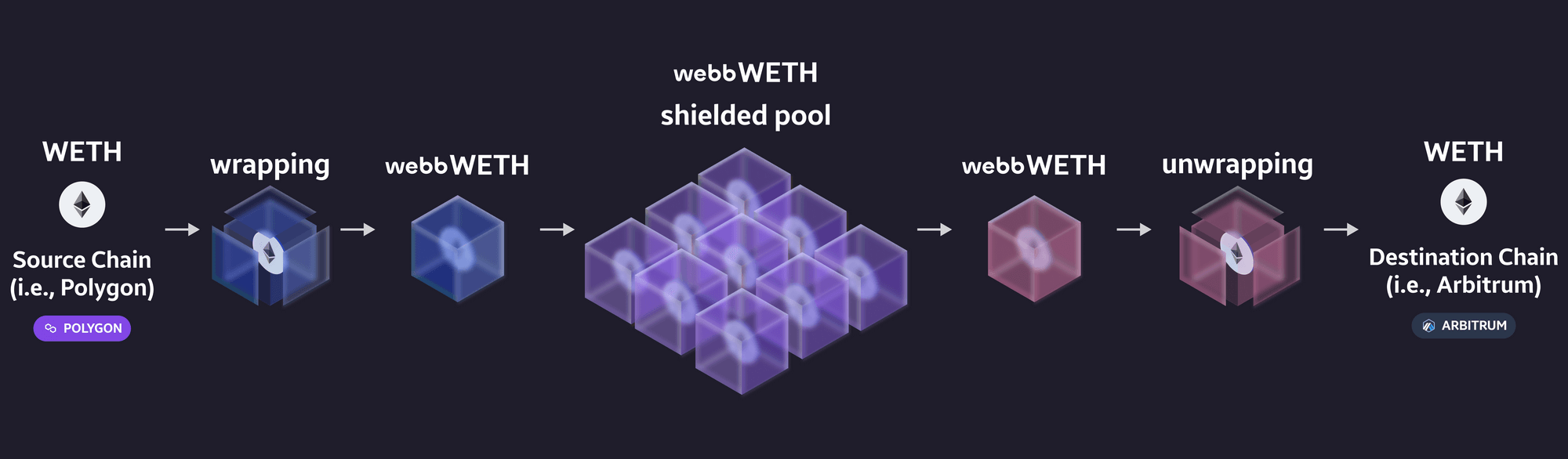
Webb’s Hubble Bridge Protocol is a paradigm shift in how blockchain bridges work. All bridge solutions send clear-text messages and rely on relayers to relay these exact plaintext messages from point-to-point. None of these solutions preserve privacy or leverage zero-knowledge proofs to scale data transfer between blockchains.
Webb’s Hubble Bridge changes that. The Hubble Bridge leverages cross-chain zero-knowledge proofs to provide full flexibility over the privacy of a message’s contents and origin location. This opens up an entirely new design space in the development of cross-chain applications, namely zero-knowledge cross-chain applications.
Firstly, it enables private cross-chain application development. Using Webb’s bridge architecture, one can build connected private applications that serve users spanning any blockchain and blockchain community in existence. Using zero-knowledge proofs, one can scale message throughput and add customizable privacy to a private cross-chain application that has never before been realized.
Zero-knowledge proofs
Webb’s bridges leverage zero-knowledge proofs to provide data provenance and authentication. When users insert secure hash-based commitments to financial data, social data, and identities into a Webb bridge, they remain the only individual with the capabilities to interact and prove properties about that data. They benefit from a shared private metric due to the fact that no observer can see, understand, or track interactions occurring over data in the bridge, no matter what side of the bridge users are interacting from.
Applications
We’ve put a lot of effort into building tools for private application development and we detail some of the applications we are planning to build out below. Some are already in active development and/or deployment.
Financial Application - Interoperable shielded pools
The natural first application for this infrastructure are private bridges for assets or what we denote as interoperable shielded pools. With Webb’s Tangle Network, we now have a decentralized and updatable system for maintaining the state of a set of bridges. Therefore, we can design the data to be inserted into these bridges around that of an asset system. Data inserted into anchors will contain UTXOs and users will be able to spend these UTXOs privately across the chains the bridge exists over using zero-knowledge proofs.
Identity Application - Interoperable membership groups
Another application we plan to extend this infrastructure towards are interoperable membership groups. Imagine communities that extend across chain and leverage privacy. A natural version of this might look like an interoperable Semaphore system, where anyone in the Semaphore membership group can relay a vote or a response to a poll from any chain privately and even without needing a wallet on that chain.
Badge Application - Interoperable badge system
Another identity based application could leverage more expressive data blobs, such as for arbitrary proofs of ownership, participation, and humanity. Using Webb’s technology stack these arbitrary badges can be proven to exist from anywhere, enabling new types of composable application development due to the zero-knowledge and private nature of the data disclosure.
Check out our docs for insights into how these systems work.
- https://docs.webb.tools/
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/anchor-system/overview/
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/protocols/asset-transfer/overview/
- https://docs.webb.tools/docs/protocols/identity/
Path forward
Webb is a cross-chain zero-knowledge messaging protocol that leverages the power of zero-knowledge proofs to provide full flexibility over the privacy of a message's contents and origin location. Using Webb's bridge architecture, connected private applications can be built that serve users spanning any blockchain and blockchain community in existence, with customizable privacy and scalable message throughput. The Tangle Network, a threshold-signature based blockchain, is a core infrastructural component of Webb's bridges and is built to serve users and operate bridges between any EVM, Substrate based blockchains, with plans to expand in the future to any other compatible blockchain ecosystem with a strong privacy need. With private bridges for assets, interoperable membership groups, and interoperable badge systems, Webb's vision is to usher in a new frontier of privacy-preserving technology for financial, identity, and social applications.
Follow us on Twitter to stay up-to-date